Grid-Tied Solar System for Your Home or Business
With photovoltaic panels on the roof, a grid-tie solar system allows a homeowner to produce electricity from sunlight. The grid-tie solar system is most common in regions where the utility company provides net metering.
Grid-tied solar systems are less expensive than off-grid solar systems alternatives and do not require battery storage. In addition, grid-tie systems can be either fixed or flexible and monitor their performance for optimization.
What is a grid-tied solar system?
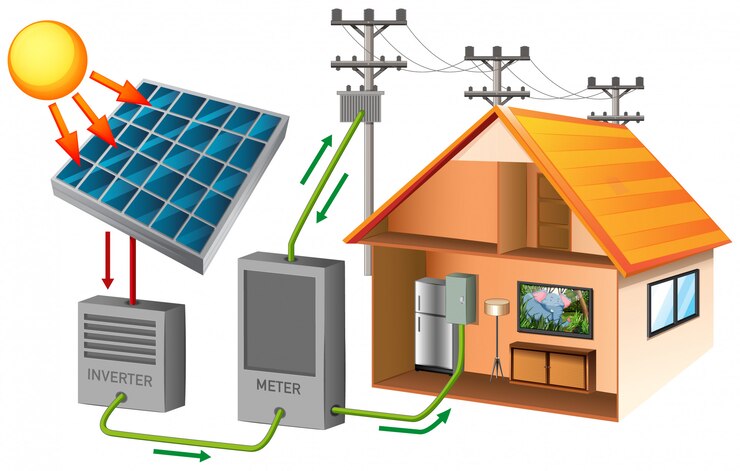
A grid-tied solar system is like having solar panels connected to your home’s electricity. It works even if you don’t have a particular battery for storing solar power. These systems are easy to use, affordable, and widely used by many people.
A grid-tied solar system goes by various names, including:
- On-grid solar system
- Grid-connect solar system
- Grid-connected solar system
- Grid-intertwined solar system
- Grid-direct solar system
How grid-tied solar systems are similar to other Solar systems
Grid-tied solar systems share standard features with other solar power systems in two key ways:
Photovoltaic (PV) Technology
- Like other solar power systems, grid-tied systems utilize photovoltaic (PV) technology.
- This means they generate electricity by harnessing sunlight through solar panels, converting it into direct current (DC) electricity.
On-Site Installation of Solar Panels
- In both grid-tied and other solar systems, solar panels are installed on-site.
- The installation is strategically done where the panels can receive ample sunlight, ensuring optimal energy production.
- The wiring of the solar panels is designed to transport the generated electricity to the system efficiently.
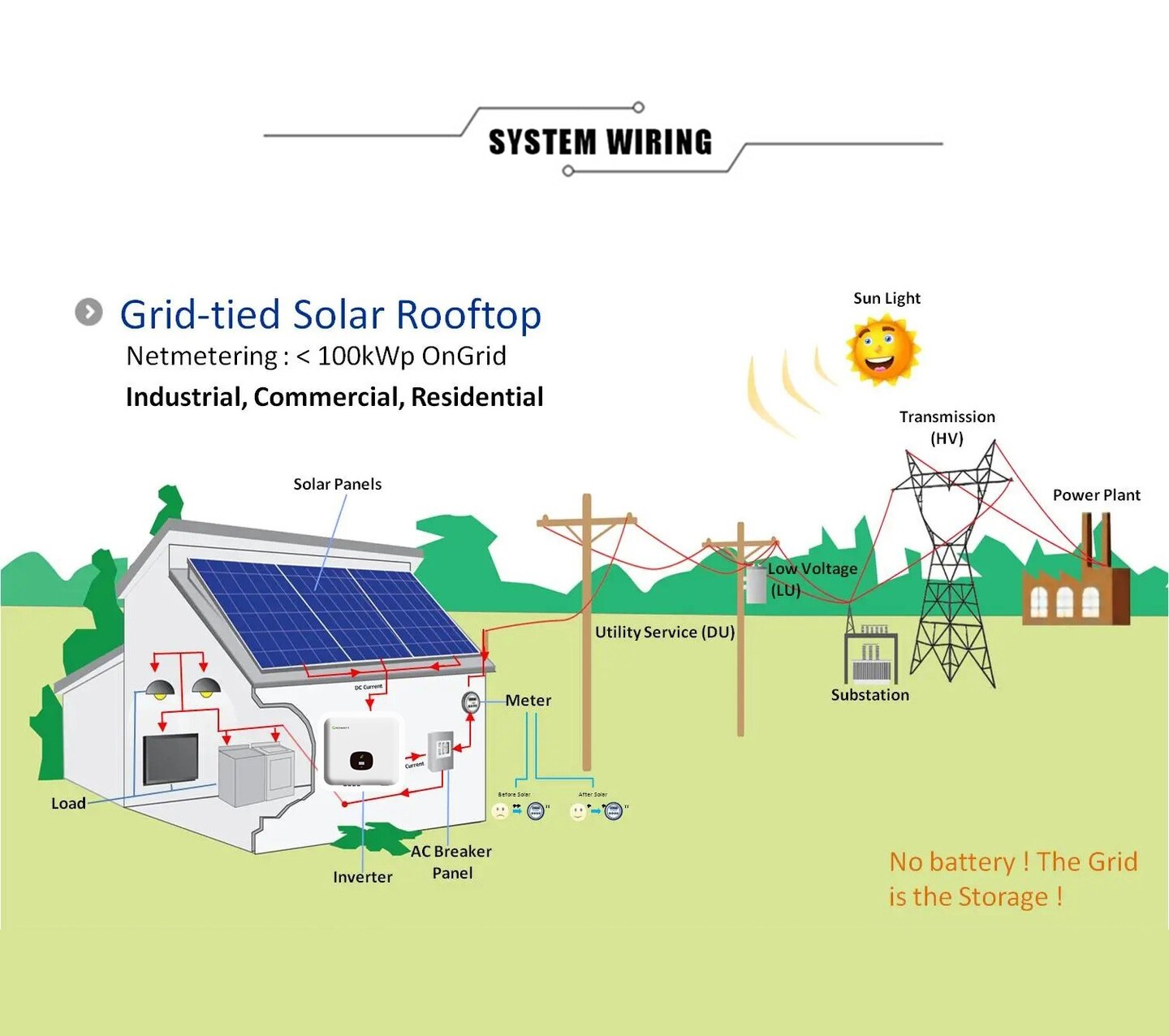
How does Grid-Tied System Works?
Grid-tied solar systems are the most common type installed in homes and businesses. They work by generating electricity from the sun and sending it to the grid. The grid then supplies the home or business with power at night or when the sun isn’t shining.
Solar panels generate DC electricity converted into AC electricity by an inverter. The AC electricity is then sent to the grid, where it can be used by homes and businesses connected to the grid. Any excess electricity generated by the solar system is sent to the grid and used by other homes and businesses.
The main benefits of grid-tied solar systems are that they’re relatively easy to install and maintain and provide a consistent renewable energy source.
Difference between other solar systems
When choosing a solar system, you’ll likely encounter three main types: grid-tied, off-grid, and hybrid systems. Let’s delve into each one to understand their unique features.
1. Grid-Tied Systems
- Connection to Main Grid: A grid-tied system connects the solar panels and the primary electricity grid.
- Dual Power Sources: This allows you to draw power from either the solar panels or the grid, providing flexibility in energy sources.
- Excess Power Feed: Grid-tied systems can automatically feed any extra solar power back into the grid.
- Different Equipment: Unique equipment is utilized compared to off-grid systems due to their interconnected nature.
2. Off-Grid Systems
- Independence from Main Grid: Unlike grid-tied systems, off-grid systems operate independently and are not connected to the primary electricity grid.
- Closed System: They function as a closed system, making them suitable for areas without access to the grid.
- Inclusion of Battery and Backup Generator: To ensure a consistent power supply, off-grid systems typically include a battery system and a backup generator.
3. Hybrid Systems
- Combination of Features: Hybrid solar systems combine elements from grid-tied and off-grid systems.
- Components: These systems include solar panels, batteries, and a grid connection, with some configurations incorporating a backup generator.
- Dynamic Energy Source Switching: Users can dynamically switch between solar power, grid power, and, in some cases, generator power based on factors like energy prices, production, and consumption.
Choosing the right solar system depends on your needs, location, and preferences. Grid-tied systems offer simplicity and cost-effectiveness, off-grid systems provide independence for remote areas, while hybrid systems offer a flexible blend of both worlds.
What are the Benefits of a Grid-Tied Solar System?
Grid-tied solar systems are widely favored for their numerous advantages, making them the most popular choice in solar setups. These benefits include:
Cost-Effective Installation
Grid-tied systems are more straightforward and require less equipment, notably because they don’t need a battery. This streamlined setup makes installation more straightforward, translating into user cost savings.
Flexible, Reliable Power
By being connected to both solar panels and the primary grid, grid-tied systems offer the benefits of solar power, such as cost-effectiveness and a reduced carbon footprint, while ensuring a continuous and reliable power supply from the grid.
Cheaper Electricity
A key advantage is the ability to feed excess electricity back into the grid. This process contributes to sustainable practices and earns credits from the energy provider, resulting in significant reductions in energy bills.
What is a Grid-tied Inverter?
A grid-tie inverter (GTI) is an electrical inverter that interfaces a photovoltaic (PV) system with the utility grid. GTIs are used in solar photovoltaic systems to change direct current (DC) electricity from the PV modules into alternating current (AC) that can be fed into the commercial power grid. GTIs can also manage power flow between the PV system and the grid, maximizing the use of PV power while minimizing stress on the grid itself.
Most GTIs will have a maximum power point tracker (MPPT) built in, which ensures that the DC input to the inverter is always at its optimal operating voltage for maximum power output. This tracking ability allows the inverter to work with various PV module types and brands.
GTIs are typically installed indoors, as they need to be protected from weather and other environmental conditions. Many GTIs have features like remote monitoring and control, alarms, and automatic shutdowns to help ensure safe and reliable operation.
What are the Disadvantages of a Grid-Tied Solar System?
There are a few disadvantages to grid-tied solar systems. One is that they rely on the utility grid, so if there is an outage, your system will not work. Another disadvantage is that grid-tied systems are usually more expensive than off-grid systems because you need to purchase additional equipment, like an inverter. Finally, grid-tied systems can be complex to install and maintain.
When to Use Off-Grid or Grid-tie Systems?
The grid-tie solar system is the most common residential solar panel system. With this system, your solar panels are connected to the utility grid. This means you can use solar power during the daytime and still have access to power from the grid at night or during a power outage.
A grid-tie system can be used with or without batteries. A grid-tie system without batteries might be a good option if you live in an area with reliable sun exposure and good grid connectivity. However, if you live in an area with less reliable sun exposure or grid connectivity, a grid-tie system with batteries might be a better option.
An off-grid solar system is the best option if you want to be completely independent of the utility grid. An off-grid system requires batteries to store solar power at night or during a power outage. Off-grid systems are more expensive than grid-tie systems because they require more equipment (batteries, inverters, etc.), but they offer true energy independence.
Grid Tied Solar Inverters
Solar panels are connected to an inverter, which converts the Direct Current (DC) generated by the solar panels into Alternating Current (AC). The AC is then fed into the home’s electrical panel, where the home’s appliances and lights can use it. Any excess AC is sent back to the utility grid.
In a grid-tied solar system, the inverter is constantly monitoring the grid for changes in frequency and voltage. When the grid goes down or if there is a power surge, the inverter will automatically shut off to protect your home and appliances from damage.
Grid-tied solar systems are less expensive than off-grid systems because you don’t need batteries to store excess electricity. You also have peace of mind knowing that you’ll still have power even if there is an outage on the grid.
How Much Does a Grid-Tied Solar System Cost?
The cost of a grid-tied solar system can vary based on factors such as the size of the system, location, and specific installation requirements. Below is an example table illustrating average costs for grid-tied solar systems of different sizes:
| Size of the System | Example of Average Costs |
|---|---|
| 4kW | $9,100 |
| 6kW | $12,390 |
| 8kW | $15,960 |
| 10kW | $19,180 |
| 12kW | $23,100 |
| 14kW | $25,480 |
| 16kW | $29,120 |
Explanation:
- Size of the System: The size of the solar system is measured in kilowatts (kW), indicating its capacity to generate electricity.
- Example of Average Costs: The costs provided in the table are examples of average expenses associated with installing varying-sized grid-tied solar systems. These costs include fees such as solar panels, inverters, mounting hardware, and installation labor.
- Cost Variations: It’s important to note that these are average costs, and actual expenses may vary based on geographical location, specific equipment chosen, and any additional customization or installation complexities.
- Economic Incentives: In some regions, there may be government incentives, tax credits, or rebates that can offset a portion of the installation costs, making solar systems more financially attractive.
- Installation Considerations: The table assumes typical installation conditions. Complexities in installation, such as roof structure, shading issues, or additional electrical work, could influence the final cost.
Considering their specific circumstances, potential solar system buyers should obtain customized quotes from solar installation professionals to get a more accurate estimate based on their unique requirements and location.
Bottom Line:
A grid-tied solar solar system is a great way to reduce your carbon footprint and save money on your energy bills. With this system, you can generate electricity and sell any excess back to the utility company. Grid-tied systems are easy to install and maintain, making them an excellent option for those who want to go green without breaking the bank.
Contact Solar Earth Inc for more info and installation for solar systems and start saving on your electricity bill today.
