Solar Inverters Types, Pros and Cons
First, let’s understand what an inverter does. Solar panels produce DC power, but household appliances run on AC power, which is what the electricity grid supplies. A Solar inverter converts the DC power from the solar panels into AC power.
The solar inverter is important for a solar system, but many people buying solar energy don’t pay attention to it. This review highlights the top inverters from leading manufacturers globally, ensuring your solar system operates smoothly for years.
How a solar inverter works?
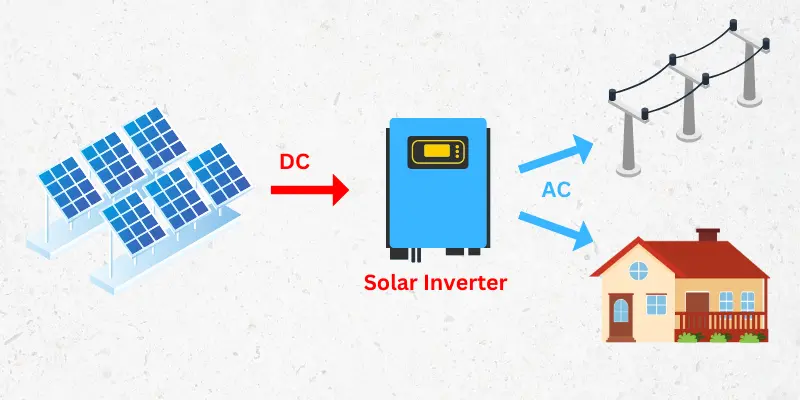
The solar inverter converts DC power from the solar panels into AC power. Home appliances can use this AC power output or send it back into the electricity grid.
Types of Solar Inverters
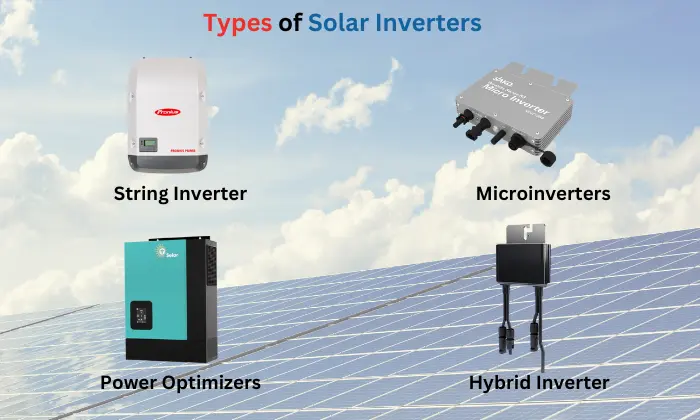
An inverter is one of the most important parts of a solar power system. However, there are alternative options for solar and energy storage systems. Below are descriptions of the four main types of inverters used for both on-grid and off-grid solar systems.
1. String Solar Inverters
This review highlights the common ‘string’ solar inverters, which are the most popular type. With these inverters, you can link up to several sets of solar panels in a row. People widely string solar inverters in the Europe and Asia. They are also becoming more famous in the US, where microinverters are already very popular.
2. Hybrid Inverters
Hybrid inverters, also called battery-ready inverters, are like string solar inverters. They can connect directly to a battery storage system. This enables greater self-sufficiency with solar power.
Hybrid inverters can provide backup power during blackouts, but they are not designed for constant off-grid use. Hybrid inverters are getting cheaper and better as technology improves and batteries become more affordable and popular. For more details, check out our best hybrid inverters review.
3. Off-grid Inverters
Off-grid power systems typically need more powerful battery inverters with built-in chargers. You can configure these as either AC or DC-coupled solar systems. Modern multi-mode inverters, which are also known as off-grid inverters, can be used to make powerful hybrid grid-connected energy storage systems.
MPPT solar charge controllers are often part of off-grid systems. They are put between the solar panels and the battery to control the charging process and keep the battery from getting too charged.
4. Microinverters
Microinverters, or micros, are small solar inverters attached directly to individual solar panels. Because each microinverter and panel works on its own, they are perfect for roofs with complicated plans and places that get shade.
Although they are slightly more expensive, microinverters are gaining popularity worldwide due to their advantages over string solar inverters. This review discusses traditional string solar inverters. However, we believe that microinverters, such as Enphase, are among the top three solar inverters. We highly recommend using them.
